 |
Omicron
4.2.0
An algorithm to detect and characterize transient events in gravitational-wave detectors
|
 |
Omicron
4.2.0
An algorithm to detect and characterize transient events in gravitational-wave detectors
|
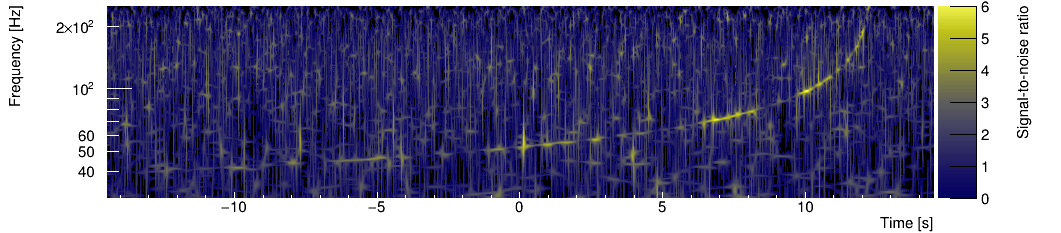
Omicron is a software analysis tool designed to perform the Q-transform of a time series. This type of time-frequency decomposition offers a multi-resolution spectrogram of the input signal. This spectrogram can be visualized in user-friendly web reports. Moreover, a signal-to-noise ratio threshold can be applied to the spectrogram pixels to produce "triggers".
Omicron has been derived from a well-known 'burst-type' search pipeline called Q-pipeline (a.k.a Omega). The original matlab code has been replaced by an optimized C++ architecture to offer a fast processing of the data. As a result, Omicron is able to process many data streams in parallel.
The Omicron package comes with a collection of user programs using Omicron libraries:
omicron-x.Omicron offers a set of C++ classes to run and visualize Q-transform analyses. The corresponding libraries can be used to develop user programs or projects:
Install Omicron from the conda-forge channel:
conda create -c conda-forge --name omicron omicron
Simply activate your omicron environment to use Omicron libraries and programs:
conda activate omicron
First, define your source and installation directories. For example:
export OMICRON_SRCDIR=${HOME}/src
export OMICRON_INSTALLDIR=${HOME}/opt/Omicron
mkdir -p ${OMICRON_SRCDIR} ${OMICRON_INSTALLDIR}You can download the Omicron source tarball from gitlab:
cd ${OMICRON_SRCDIR}
wget https://git.ligo.org/virgo/virgoapp/Omicron/-/archive/[X.Y.Z]/Omicron-[X.Y.Z].tar.gz
tar -xzf Omicron-[X.Y.Z].tar.gz where [X.Y.Z] is the Omicron version of your choice.
Alternatively, you can get a development copy of the Omicron software using git and select a release tag:
cd ${OMICRON_SRCDIR}
git clone https://git.ligo.org/virgo/virgoapp/Omicron.git
cd Omicron/
git checkout [X.Y.Z]The Omicron package relies on several external packages which you must install on your machine:
Here, we give step-by-step instructions to build Omicron for UNIX (bash/sh) systems.
# go to the source directory
cd ${OMICRON_SRCDIR}/Omicron/
# create the build directory
mkdir ./build/; cd ./build/
# configure Omicron
cmake -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=${OMICRON_INSTALLDIR} ${OMICRON_SRCDIR}/Omicron
# compile Omicron
make
# install Omicron
make install
An environment script has been generated. It must be sourced before using Omicron:
source ${OMICRON_INSTALLDIR}/etc/omicron.env.sh
You can test that Omicron is correctly installed by typing:
omicron version
If you have the Doxygen software installed in your machine, you can access Omicron documentation with a web browser at file://${OMICRON_INSTALLDIR}/share/doc/Omicron/html/index.html.
See all documentation pages in the Related Pages
Florent Robinet - Laboratoire de Physique des 2 Infinis Irène Joliot-Curie (IJCLab) Orsay, France - contact